shell脚本——shell编程规范与变量
本文共 1935 字,大约阅读时间需要 6 分钟。
shell脚本——shell编程规范与变量
一、shell脚本概述
1、shell的概念
- shell脚本(Shell Script)就是将要执行的命令按顺序保存到一个文本文件,并给该文件可执行权限,方便一次性执行的一个程序文件。主要是方便管理员进行设置或管理,可结合各种shell控制语句以完成更复杂的操作。
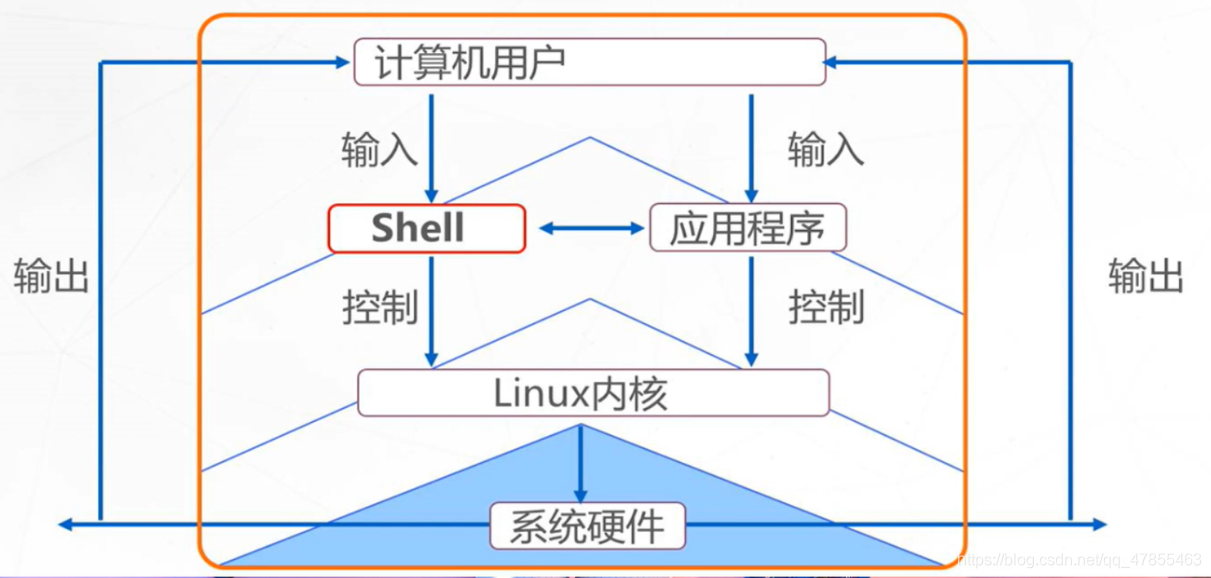
2、shell的作用——“命令翻译器”
- 介于系统内核与用户之间,负责解释命令行,将需要的执行操作传递给内核执行,并输出执行结果
3、shell脚本应用场景
- 重复性操作
- 交互性任务
- 批量事务处理
- 服务运行状态监控
- 定时任务执行
二、shell编程规范
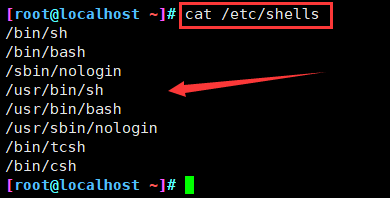
1、用户登录shell
- 登录后默认使用的shell程序,一般为/bin/bash
- 不同shell的内部指令、运行环境等会有所不同
| shell | 说明 |
|---|---|
| bash | $基准于GNU的框架下发展出的shell |
| csh | 语法有点类似于C语言的shell |
| tcsh | 整合了csh,提供更多的功能 |
| sh | 已经被bash所替换 |
| nologin | 奇怪的shell,这个shell可以让用户无法登录主机 |
2、shell脚本的组成
- 脚本申明(解释器):若第一行为“#!/bin/bash” ,表示此行一下的代码语句是通过/bin/bash程序来结实执行,#!/bin/bash为默认解释器,还有其他类型的解释器,比如#!/usr/bin/python、#!/usr/bin/expect。
- 注释信息:以“#”开头的语句表示为注释信息,被注释的语句在运行脚本时将不被执行。
- 可执行语句:比如echo命令,用于输出“ ”之间的字符串。

3、shell脚本的执行
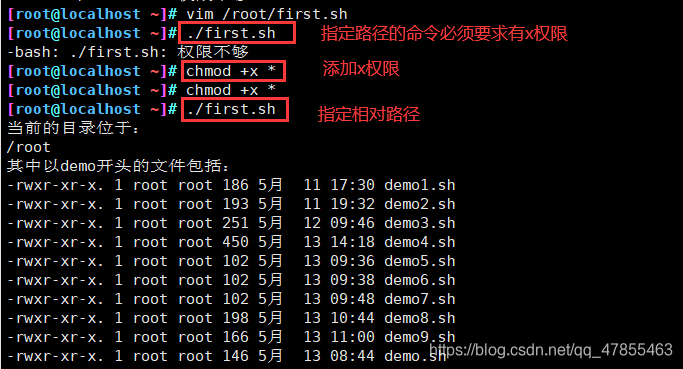
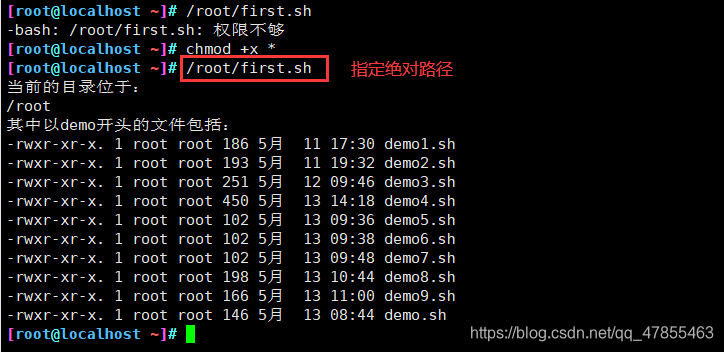
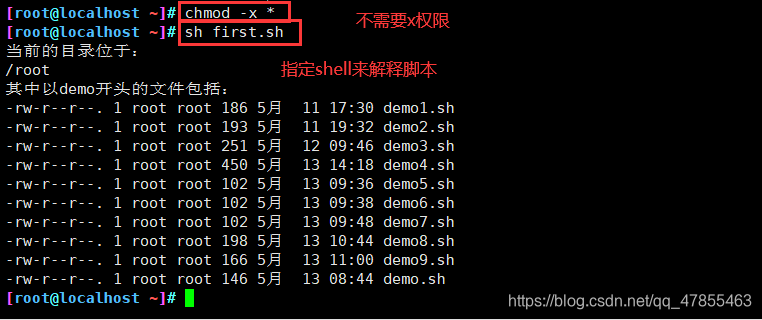
方法一:指定路径的命令,要求文件必须有x权限
- 指定绝对路径:/root/first.sh
- 指定相对路径:./first.sh
方法二:指定shell来解释脚本,不要求文件必须有x权限
- sh 脚本路径:sh first.sh
- source 脚本路径:.first.sh 或者source first.sh
三、管道
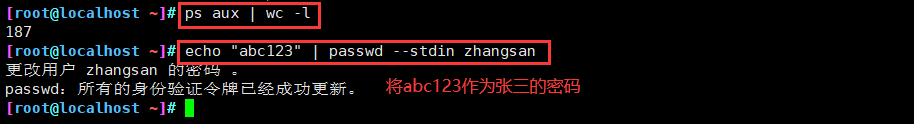
1、管道格式
- 将管道符号“|”左侧的命令输出的结果,作为右侧命令的输入(处理对象),同一行命令中可以使用多个管道 使用格式
cmd1 命令1 | cmd2 命令2[... | cmdn 命令n]
2、管道操作
四、重定向
1、重定向的几类交互设备文件
- 标准输入:从该设备接收用户输入的数据
- 标准输出:通过该设备向用户输出数据
- 标准错误:通过该设备报告执行出错信息
| 类型 | 设备文件 | 文件描述编号 | 默认设备 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 标准输入 | /dev/stdin | 0 | 键盘 |
| 标准输出 | /dev/stdout | 1 | 显示器 |
| 标准错误输出 | /dev/stderr | 2 | 显示器 |
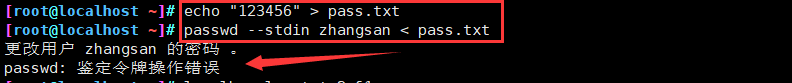
2、重定向操作
| 类型 | 操作符 | 用途 |
|---|---|---|
| 重定向输入 | < | 从指定的文件读取数据 |
| 重定向输出 | > | 将标准输出结果 保存 到指定的文件,并且覆盖原有内容 |
| - | >> | 将标准输出结果 追加 到指定的文件的尾部,不覆盖原有内容 |
| 标准错误输出 | 2> | 将错误信息 保存 到指定的文件,并且覆盖原有内容 |
| - | 2>> | 将错误信息 追加 到指定的文件的尾部,不覆盖原有内容 |
| 混合输出 | &> | 将标准输出、标准错误保存到同一文件中 |
| - | 2>&1 | 将标准错误输出重定向到标准输出 |
五、shell脚本变量
1、变量的作用
- 用来存放系统和用户需要使用的特定参数(值)
- 变量名:使用固定的名称,由系统预设或用户定义
- 变量值: 能够根据用户设置、系统环境的变化而变化
2、变量的类型
- 自定义变量:由用户自定义、修改和使用
- 特殊变量:环境变量,只读变量,位置变量,预定义变量
- 环境变量:由系统维护,用于设置工作环境
- 只读变量:用于变量值不允许被修改的情况
- 位置变量:通过命令行给脚本程序传递参数
- 预定义变量:bash中内置的一类变量,不能直接修改
六、shell脚本变量——自定义变量
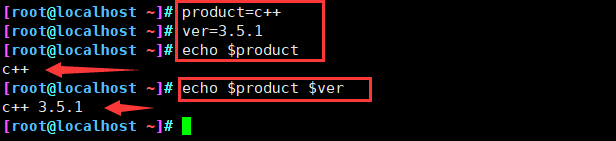
1、定义一个新变量
- 变量名以字母或下划线开头,区分大小写,建议全大写
变量名=变量值
2、查看变量值
echo $变量名
3、赋值时使用引号
| 引号 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 双引号 | 允许通过$符号引用其他变量 |
| 单引号 | 禁止引用其他变量值,$视为普通字符 |
| 反撇号 | 命令替换,提取命令执行后的输出结果 |
4、从键盘输入内容为变量赋值
--------方法一---------read [-p "提示信息"] 变量名echo $变量名--------方法二---------read 变量名echo $变量名
5、变量作用范围
- 默认情况下,新定义的变量只在当前的shell环境中有效,因此成为局部变量。当进入子程序或新的子shell环境中时,局部变量将无法再使用
- 可以
七、shell脚本变量——特殊变量
转载地址:http://riphz.baihongyu.com/
你可能感兴趣的文章
Mysql 中的日期时间字符串查询
查看>>
mysql 中索引的问题
查看>>
MySQL 中锁的面试题总结
查看>>
MySQL 中随机抽样:order by rand limit 的替代方案
查看>>
MySQL 为什么需要两阶段提交?
查看>>
mysql 为某个字段的值加前缀、去掉前缀
查看>>
mysql 主从
查看>>
mysql 主从 lock_mysql 主从同步权限mysql 行锁的实现
查看>>
mysql 主从互备份_mysql互为主从实战设置详解及自动化备份(Centos7.2)
查看>>
mysql 主从关系切换
查看>>
MYSQL 主从同步文档的大坑
查看>>
mysql 主键重复则覆盖_数据库主键不能重复
查看>>
Mysql 事务知识点与优化建议
查看>>
Mysql 优化 or
查看>>
mysql 优化器 key_mysql – 选择*和查询优化器
查看>>
MySQL 优化:Explain 执行计划详解
查看>>
Mysql 会导致锁表的语法
查看>>
mysql 使用sql文件恢复数据库
查看>>
mysql 修改默认字符集为utf8
查看>>
Mysql 共享锁
查看>>